The Future of Transportation in Uttar Pradesh: Readying for a Paradigm Shift
- admin
- December 18, 2025
- Development, travel
- 0 Comments
Uttar Pradesh (UP), India’s most populous state, is embarking on a transformative journey in its transportation sector. Anchored in extensive infrastructure modernization, the adoption of clean energy alternatives, and the integration of cutting-edge technologies, the state is positioning itself for a sustainable and efficient future. However, the readiness of UP to adapt to these monumental changes invites a critical assessment.
Current Infrastructure and Operational Dynamics
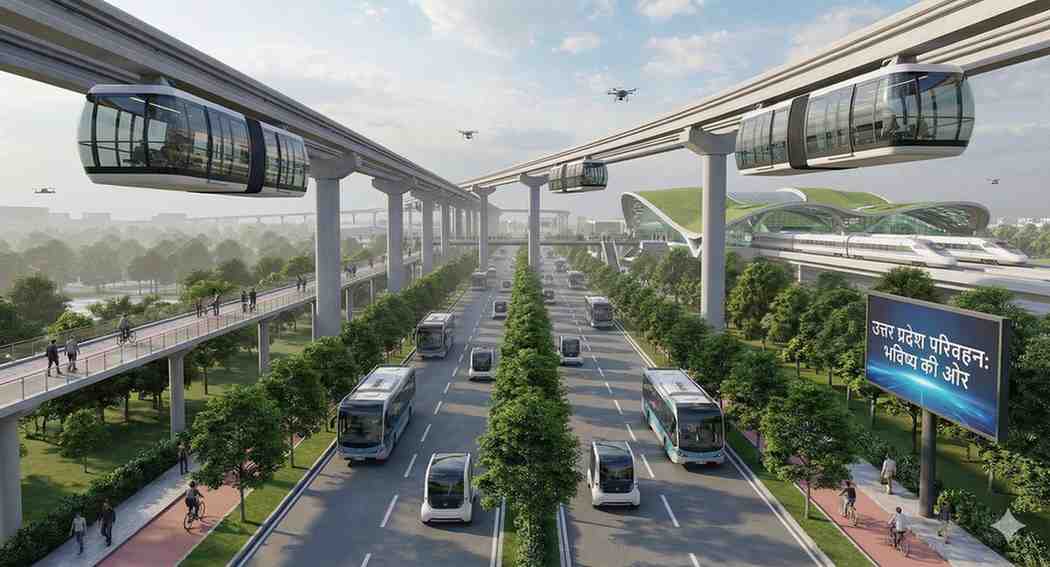
The transportation matrix of Uttar Pradesh encapsulates a juxtaposition of traditional systems and emerging modern mechanisms. According to the Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (UPSRTC), public buses cater to over 12 million commuters daily, underlining their pivotal role in state mobility. The state’s highway network, spanning more than 8,600 kilometers—the longest in India—is a vital contributor to national connectivity, as documented by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
The Indian Railways’ network in Uttar Pradesh is equally significant, with strategic freight and passenger routes traversing the region. Stations like Kanpur Central and Lucknow Junction are integral to this infrastructure, facilitating millions of passengers annually, as per Indian Railways’ operational data.
On the aviation front, Chaudhary Charan Singh International Airport (Lucknow) and Lal Bahadur Shastri Airport (Varanasi) have witnessed exponential growth in passenger numbers. The impending launch of Noida International Airport at Jewar, anticipated to be among Asia’s largest, is poised to recalibrate air travel dynamics in the region.
Transformative Developments: Catalysts for Change
1. Expressway Expansion
Uttar Pradesh has emerged as a frontrunner in India’s expressway revolution. Mega-projects like the Purvanchal Expressway (341 km), Bundelkhand Expressway (296 km), and the upcoming Ganga Expressway (594 km) aim to enhance regional connectivity and spur economic development. According to the Uttar Pradesh Expressways Industrial Development Authority (UPEIDA), these expressways incorporate intelligent traffic management systems and automated toll collection frameworks, epitomizing next-generation infrastructure.
2. Metro Rail Advancements
The Uttar Pradesh Metro Rail Corporation (UPMRC) has achieved substantial milestones in urban transport. For instance, the Lucknow Metro, serving over 60,000 daily passengers, exemplifies the role of modern transit in alleviating congestion. Expansion initiatives targeting Varanasi and Meerut aim to bolster urban mobility further, in alignment with UPMRC’s strategic blueprint.
3. Electric Mobility Initiatives
The Uttar Pradesh Electric Vehicle (EV) Policy 2022 underscores the state’s commitment to environmental sustainability. With plans to install 20,000 EV charging stations and electrify 70% of public transport by 2030, the policy envisions a 40% reduction in urban vehicular emissions, as projected by the state’s Department of Energy.
4. Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS)
The Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut RRTS corridor, managed by the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC), represents a paradigm shift in high-speed regional travel. Expected to slash travel times between Delhi and Meerut to under an hour, this corridor exemplifies the state’s dedication to futuristic transit solutions.
Persistent Challenges
Despite these advancements, Uttar Pradesh grapples with significant obstacles:
- Urban Congestion: Urban centers like Kanpur and Varanasi face acute traffic gridlocks exacerbated by limited parking infrastructure and insufficient public transit management.
- Rural Accessibility: While expressway connectivity has improved, rural regions continue to suffer from inadequate last-mile transport solutions, necessitating enhanced UPSRTC outreach.
- Environmental Impact: Data from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) attributes 40% of urban air pollution in Uttar Pradesh to vehicular emissions, highlighting the urgency of expedited EV adoption.
- Fiscal and Operational Bottlenecks: The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has flagged issues such as budget overruns and project delays, undermining the potential impact of key infrastructure ventures.
Strategic Vision: Building an Inclusive Future
To effectively navigate its transformative ambitions, Uttar Pradesh must integrate the following strategies:
- Technological Integration: Employing Artificial Intelligence (AI) for dynamic traffic management and predictive maintenance can optimize infrastructure efficiency.
- Sustainability: Accelerating the EV transition and integrating renewable energy sources into the transport ecosystem are critical to mitigating environmental challenges.
- Equitable Planning: Ensuring robust last-mile connectivity and prioritizing underserved rural regions will foster inclusive development.
- Public Engagement: Promoting a cultural shift toward public transport through awareness initiatives and incentive programs will be instrumental in reducing reliance on private vehicles.
Conclusion
Uttar Pradesh stands at the threshold of a transformative era in transportation, driven by visionary projects and technological advancements. However, the realization of this vision hinges on addressing urban congestion, enhancing rural connectivity, and mitigating environmental concerns. By championing innovation alongside inclusivity, the state has the potential to redefine its transportation landscape, setting a benchmark for progressive and sustainable development in India.