How Uttar Pradesh Is Shaping Its Future Through Smart City Initiatives
- admin
- September 27, 2025
- Development, Government
- 0 Comments
Key Highlights:
- Uttar Pradesh is investing ₹16,000 crore in its Smart Cities Mission by 2025, transforming 6 cities into model urban centers.
- Lucknow, Agra, Varanasi, Prayagraj, Kanpur, and Meerut are the six cities earmarked for smart city transformation.
- Smart traffic management systems and solar-powered streetlights are central to the smart city projects in Uttar Pradesh.
- The Agra Smart City Project has led to improvements in waste management and digital traffic solutions.
Introduction
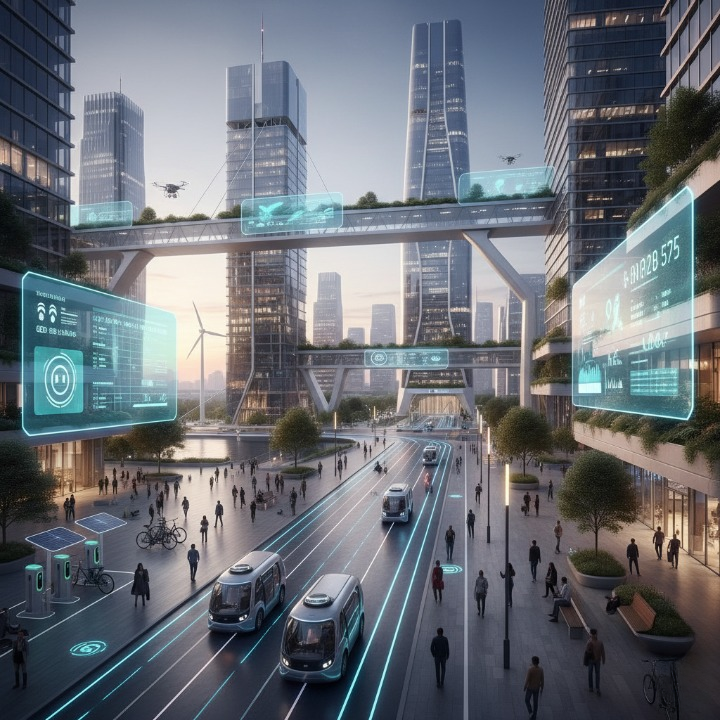
As Uttar Pradesh undergoes a transformative journey to modernize its urban infrastructure, the focus is on harnessing technology and innovation to improve the lives of its residents. Through the Smart Cities Mission, launched by the Government of India, the state is embracing a forward-thinking approach to urban planning and governance. With six cities in Uttar Pradesh being developed as smart cities, the state is strategically investing in sustainable infrastructure, digital governance, and green technologies to create urban spaces that are not only smarter but also more sustainable and inclusive.
Uttar Pradesh’s smart city initiatives are designed to address critical urban challenges, such as congestion, pollution, inefficient public services, and lack of infrastructure, while providing solutions that improve the quality of life for millions of residents.
The Smart Cities Mission in Uttar Pradesh: Transforming Urban Spaces
- Lucknow: Leading the Smart City Transformation
Lucknow, the state capital, is a flagship city under the Smart Cities Mission, with an emphasis on infrastructure modernization, smart transportation, and green technologies. The city is introducing smart traffic management systems that use sensors and cameras to monitor and control traffic, reducing congestion and improving the flow of vehicles.
Additionally, solar-powered streetlights are being installed throughout the city, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency. Lucknow is also focusing on digital governance with the launch of online platforms for residents to access government services, pay bills, and submit grievances, making local government more accessible and efficient.
- Agra: Enhancing Sustainability and Efficiency
Agra, one of India’s most visited cities due to the Taj Mahal, is utilizing smart city initiatives to enhance its infrastructure while preserving its rich cultural heritage. Agra’s smart city plan focuses on smart waste management, which includes the use of waste-to-energy plants and intelligent waste bins that notify authorities when they need to be emptied.
Another key aspect of Agra’s smart city transformation is smart traffic systems, which aim to reduce congestion around the city’s tourist hotspots and improve the visitor experience. These measures are part of a broader push to integrate sustainable technologies while improving urban living standards for Agra’s residents.
- Varanasi: A Blend of Heritage and Technology
As one of the oldest cities in the world, Varanasi is balancing its ancient cultural identity with modern smart city technologies. The city has focused on sustainable urban development, with projects that integrate rainwater harvesting, solar energy, and energy-efficient buildings.
The Ganga riverfront development has been central to this transformation, with the introduction of advanced water management systems to reduce water wastage and improve the cleanliness of the riverfront. Additionally, electric buses and smart public transport systems are being implemented to enhance mobility and reduce air pollution.
Core Components of Smart City Development in Uttar Pradesh
- Sustainable Transportation
A central feature of Uttar Pradesh’s smart cities is the integration of sustainable transportation systems. This includes the Lucknow Metro, which has significantly improved urban mobility, and electric buses in cities like Varanasi and Agra. These initiatives aim to reduce the dependency on fossil fuel-powered vehicles, lowering pollution levels and reducing traffic congestion in busy urban areas.
The development of dedicated bus lanes and cycle tracks is also a priority, encouraging green modes of transportation and making cities more pedestrian-friendly.
- Renewable Energy Integration
Renewable energy is a cornerstone of Uttar Pradesh’s smart city strategy. Solar-powered streetlights, solar rooftops, and energy-efficient buildings are key components of the smart city projects. The integration of solar panels into the urban landscape reduces dependency on conventional power sources, promotes energy conservation, and contributes to the state’s renewable energy targets.
In cities like Lucknow and Agra, solar farms are being developed to meet a significant portion of the cities’ energy needs, helping to lower carbon emissions while ensuring a sustainable energy future.
- Smart Governance and Digital Services
The transition to digital governance is integral to Uttar Pradesh’s smart city vision. Cities like Lucknow and Kanpur are implementing e-governance platforms, where citizens can access essential services online, such as paying utility bills, applying for permits, and participating in local decision-making processes.
These platforms reduce bureaucracy, make government services more transparent, and improve the efficiency of service delivery. Additionally, citizen engagement apps allow residents to directly communicate with city officials, report issues, and offer feedback on urban services.
- Water and Waste Management
Efficient water and waste management systems are essential for making cities livable and sustainable. Smart cities in Uttar Pradesh are adopting automated water meters and waste management systems that monitor consumption, reduce wastage, and ensure timely waste collection. The use of smart sensors in waste bins and sewage systems helps city authorities monitor waste levels and prevent blockages or overflow.
In Agra, the integration of waste-to-energy plants is reducing landfill waste and turning it into useful energy, which can power public services.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While Uttar Pradesh’s smart city initiatives are advancing, there are several challenges:
- Infrastructure Funding:
Smart city projects require significant investments in infrastructure, which can be difficult to fund through public sources alone. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are key to attracting investments and ensuring that these projects remain financially viable in the long term. - Bridging the Digital Divide:
Ensuring that all segments of the population have access to the digital services provided by smart cities is essential. The state must focus on digital literacy programs and ensuring that marginalized communities have the tools and knowledge to access e-governance platforms and other digital services. - Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
As smart cities grow, it’s crucial that they are built in a way that minimizes environmental impacts. The state will need to continue prioritizing sustainable construction practices and ensure that new developments meet green standards.
Conclusion
Uttar Pradesh’s smart city initiatives are setting the stage for a modern, sustainable urban future. By focusing on sustainable infrastructure, green technologies, digital governance, and inclusive growth, the state is transforming its urban spaces to meet the demands of the 21st century. While challenges remain, the ambitious efforts underway in cities like Lucknow, Agra, and Varanasi show that Uttar Pradesh is well on its way to becoming a leader in India’s urban transformation.
By continuing to invest in infrastructure, technology, and citizen-centric policies, Uttar Pradesh will create cities that are not only smarter but also more resilient, inclusive, and sustainable in the long term.
Sources:
- Uttar Pradesh Smart Cities Mission
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India
- Uttar Pradesh State Government
- Uttar Pradesh Smart City Development Corporation