The Crucial Role of Caste in UP Politics: A Game Changer for Parties
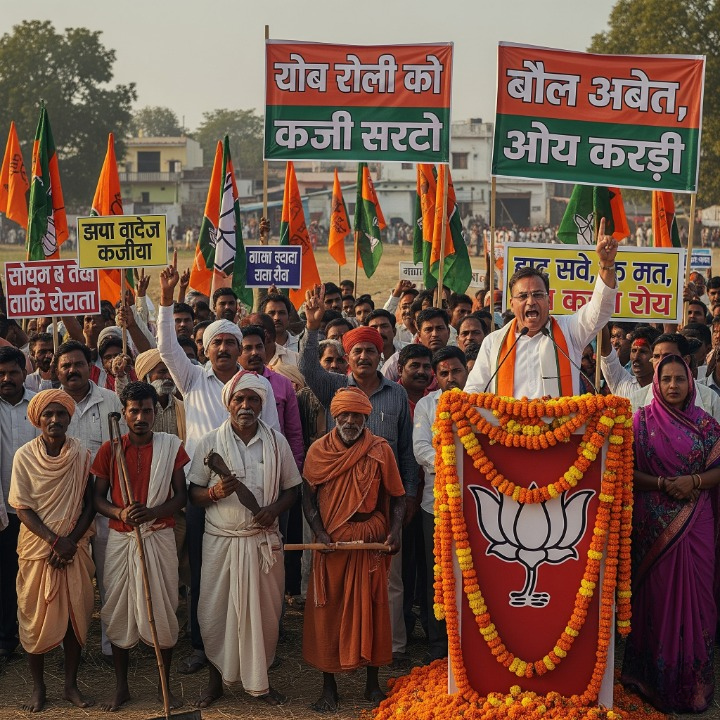
Lucknow, 2025 — Uttar Pradesh (UP), often seen as the political heartland of India, holds a unique distinction in the nation’s electoral landscape due to its deeply entrenched caste dynamics. For decades, caste has remained the most significant factor shaping political strategies, alliances, and outcomes in the state. This article examines how caste continues to be a game changer for political parties in UP and its broader implications for Indian democracy.
The Caste Landscape in UP
- Major Caste Groups
- Dalits (Scheduled Castes): Constituting nearly 21% of the population, Dalits form a critical vote bank. The Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) has historically championed Dalit causes, positioning itself as their primary representative.
- Other Backward Classes (OBCs): OBCs make up about 40% of UP’s population, with sub-castes like Yadavs, Kurmis, and Lodhs playing decisive roles in elections.
- Upper Castes: Brahmins, Rajputs, and others comprise approximately 18%, wielding considerable influence in both politics and governance.
- Minorities: Muslims, while primarily a religious group, often align along caste identities like Ansaris and Qureshis, adding complexity to the political calculus.
- Caste Coalitions
- Dominant Alliances: Political parties rely on strategic caste alliances, such as the Yadav-Muslim equation for the Samajwadi Party (SP) or the OBC-upper caste coalition led by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP).
- Changing Dynamics: With caste identities evolving, parties are increasingly focusing on sub-castes to carve out new voter bases.
The Role of Caste in Political Strategies
- Election Campaigns
- Targeted Messaging: Parties craft caste-specific manifestos and promises, ranging from reservation benefits to welfare schemes, tailored to resonate with specific communities.
- Leaders and Candidates: Ticket distribution heavily favors caste dynamics, ensuring representation from key communities in every constituency.
- Welfare Schemes
- Focused Benefits: Programs like free housing, scholarships, and employment schemes are often designed to appeal to particular castes.
- Impact: Welfare policies aimed at specific groups help solidify party loyalty among caste-based voter blocs.
- Caste-Based Polarization
- Political Rhetoric: Caste remains a central theme in political speeches and narratives, often deepening divides for electoral gains.
- Implications: While it secures short-term victories, caste polarization can hinder long-term social cohesion.
Key Political Players and Caste Politics
- Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
- Strategy: The BJP’s formula of combining upper castes and non-Yadav OBCs has proven successful in recent elections.
- Challenge: Maintaining this coalition while addressing aspirations of individual caste groups.
- Samajwadi Party (SP)
- Focus: The SP has relied on its Yadav-Muslim base but is now working to expand its appeal among non-Yadav OBCs and upper castes.
- Tactics: Leveraging community leaders to rebuild trust among diverse groups.
- Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP)
- Core Base: The BSP’s Dalit-centric approach faces challenges in regaining its former glory as other parties woo Dalit sub-castes.
- Vision: Reviving its image as a party for the marginalized through grassroots mobilization.
- Congress
- Rebuilding Efforts: The Congress is attempting to reclaim lost ground by appealing to Brahmins and Dalit communities with inclusive policies.
- Hurdle: Reestablishing trust in a state dominated by regional and national players.
Challenges of Caste Politics
- Social Fragmentation
- Issue: Overemphasis on caste identities often exacerbates societal divides, hindering broader social unity.
- Solution: Promoting policies that transcend caste lines while addressing systemic inequalities.
- Changing Aspirations
- Emerging Trends: Younger voters increasingly prioritize development and employment over traditional caste loyalties.
- Adaptation: Parties must balance caste-based strategies with broader developmental agendas.
Conclusion: A Persistent Influence
Caste remains a cornerstone of UP’s political framework, shaping alliances, policies, and electoral outcomes. While its role as a game changer for parties is undeniable, the state’s future may hinge on balancing caste considerations with inclusive development and social harmony. As UP continues to be a bellwether for Indian politics, how it navigates the complexities of caste dynamics will have far-reaching implications for the nation’s democratic fabric.