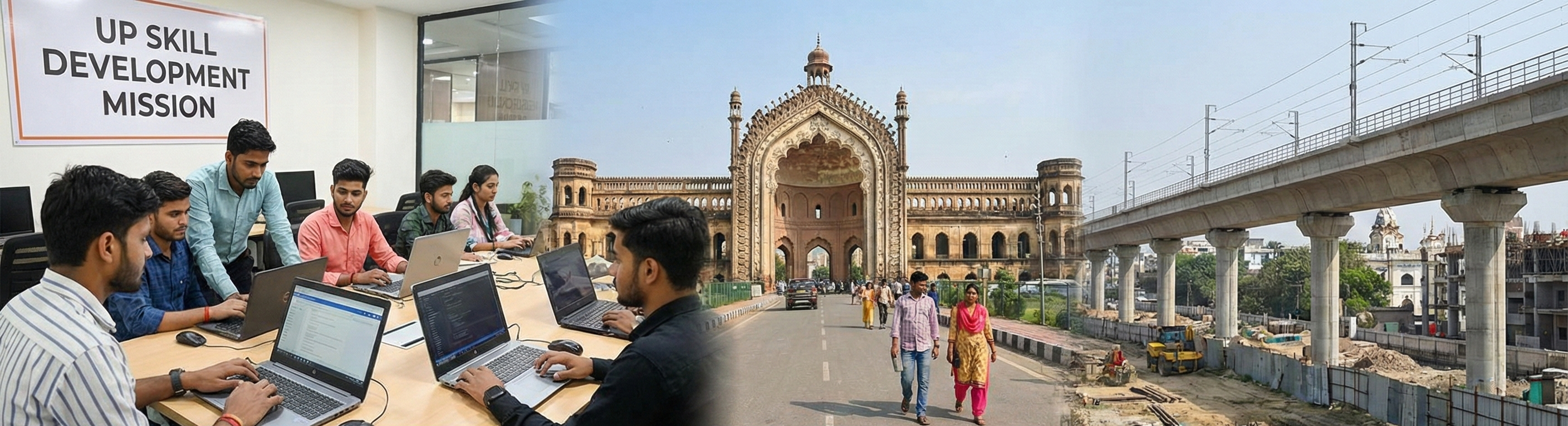
The Future of Youth Employment in Uttar Pradesh: A Comprehensive Analysis
- admin
- December 20, 2025
- Capital Journal
- 0 Comments
Uttar Pradesh (UP), India’s most populous state, is characterized by a dynamic and burgeoning youth demographic. With over 60% of its 200-million-plus residents under the age of 30, the state’s demographic dividend presents both a transformative opportunity and a profound challenge. While the potential for fostering robust economic growth is immense, ensuring that this youth cohort has access to meaningful and sustainable employment remains a pivotal issue. This raises an essential question: Are existing strategies sufficient to guarantee a secure employment landscape for Uttar Pradesh’s youth?
Current Employment Landscape
1. Demographics and Labor Market Dynamics
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) 2022 reports that Uttar Pradesh’s unemployment rate stands at 4.2%, marginally below the national average of 4.8%. However, the youth unemployment rate for the 15-29 age group significantly exceeds this, reaching 12.9%. This disparity underscores the necessity for targeted, youth-centric employment interventions to address the structural and systemic barriers confronting young job seekers.
2. Key Sectors and Emerging Opportunities
The state’s economy remains predominantly agrarian, with nearly 45% of its workforce engaged in agriculture. Nonetheless, emerging sectors such as manufacturing, services, and information technology are gaining traction. Strategic initiatives like the Uttar Pradesh Defence Corridor and the One District One Product (ODOP) scheme aim to catalyze industrial growth, promote local craftsmanship, and create diversified employment opportunities for the youth.
3. Education and Employability
Despite hosting prestigious institutions such as the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur and Banaras Hindu University (BHU), Uttar Pradesh faces substantial challenges in bridging the gap between educational outcomes and labor market demands. A Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) report reveals that only 34% of the state’s youth possess skills deemed relevant to current market needs, highlighting a critical mismatch that impedes employment readiness.
Policy and Programmatic Interventions
1. Skill Development Initiatives
The Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM) aims to train 4 million youth annually across various sectors, including healthcare, information technology, and construction. The Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), implemented in collaboration with state authorities, complements these efforts by offering certification-based training designed to enhance employability.
2. Fostering Entrepreneurship
The state government’s Start-Up Policy 2020, under the broader Start-Up India initiative, has facilitated the establishment of incubation centers and allocated seed funding to over 800 start-ups. This policy envisions the creation of 100,000 direct jobs by cultivating a robust entrepreneurial ecosystem.
3. Industrial Investment and Growth
Efforts to attract industrial investment include the organization of the Investors Summit, which secured Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) worth over ₹2 lakh crore in 2022. Key sectors prioritized for job creation include textiles, electronics, and renewable energy. The Uttar Pradesh Defence Corridor alone is projected to generate over 250,000 employment opportunities in the coming years.
Persistent Challenges
- Underemployment and Informality: Despite moderate overall unemployment rates, underemployment and reliance on the informal sector are widespread. Approximately 80% of Uttar Pradesh’s workforce is employed informally, characterized by limited job security and lack of benefits.
- Urban-Rural Employment Divide: Employment opportunities remain disproportionately concentrated in urban centers, leaving rural youth with fewer prospects. Inadequate transport and digital infrastructure further exacerbate this divide.
- Gender Disparities: Female labor force participation in Uttar Pradesh is among the lowest in India, with only 16% of women actively engaged in the workforce, as per PLFS 2022. Addressing gender-specific barriers is critical for achieving inclusive economic growth.
- Skill and Demand Mismatch: A National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) survey reveals a significant disconnect between skills imparted by educational and vocational training programs and those demanded by the labor market, necessitating systemic reforms.
Strategic Recommendations for Youth Employment
- Expanding Vocational Training Programs: Scaling vocational training programs tailored to high-growth industries, including digital technologies and green energy, can enhance youth employability.
- Rural Employment Initiatives: Complementing the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) with initiatives to create sustainable non-agricultural employment in rural areas is essential.
- Strengthening Public-Private Partnerships: Fostering collaboration between academic institutions, industries, and government agencies can bridge the skill gap and align training programs with market demands.
- Inclusive Workforce Policies: Initiatives aimed at increasing female workforce participation—including flexible work arrangements, childcare support, and targeted awareness campaigns—must be prioritized.
- Start-Up Ecosystem Enhancement: Offering mentorship, financial incentives, and streamlined access to markets for start-ups can stimulate entrepreneurial ventures and drive job creation.
Conclusion
Uttar Pradesh’s expansive youth demographic represents an unparalleled asset for fostering economic growth and innovation. However, realizing this potential necessitates concerted and strategic action to address persistent challenges such as underemployment, skill mismatches, and gender disparities. While initiatives like UPSDM and ODOP provide a solid foundation, scaling these programs and integrating innovative approaches are imperative. By cultivating a conducive environment for education, entrepreneurship, and industrial expansion, Uttar Pradesh can secure a prosperous future for its youth while setting a precedent for other states grappling with similar challenges.