The Impact of Education Reforms on Uttar Pradesh’s Future Workforce
- admin
- December 9, 2025
- Education, Uttar Pradesh
- 0 Comments
Uttar Pradesh (UP), India’s most populous state, has long grappled with significant challenges in its education sector. High dropout rates, uneven access, and quality disparities between urban and rural schools have hindered the development of a skilled and employable workforce. To address these issues, the state government has implemented a series of education reforms. This analysis examines the effectiveness of these initiatives in shaping UP’s future workforce through a detailed exploration of key reforms, their impact, and existing challenges.
Education Reforms: Key Initiatives
1. Operation Kayakalp
Operation Kayakalp, launched in 2018, focuses on modernizing government schools by addressing foundational infrastructure gaps. Data from the Uttar Pradesh Basic Education Department indicates that over 1.5 lakh schools have been upgraded with essential facilities such as functional toilets, boundary walls, electricity, and clean drinking water. This initiative aims to provide a conducive learning environment, particularly in underserved rural areas.
2. Digital Education Transformation
The state’s push towards digital education aligns with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasizes technology integration in classrooms. Through the Prerna Initiative, smart classrooms equipped with tablets, projectors, and e-learning modules have been introduced in over 10,000 schools. These efforts seek to bridge the digital literacy gap and foster technology-driven learning.
3. Vocational Training Integration
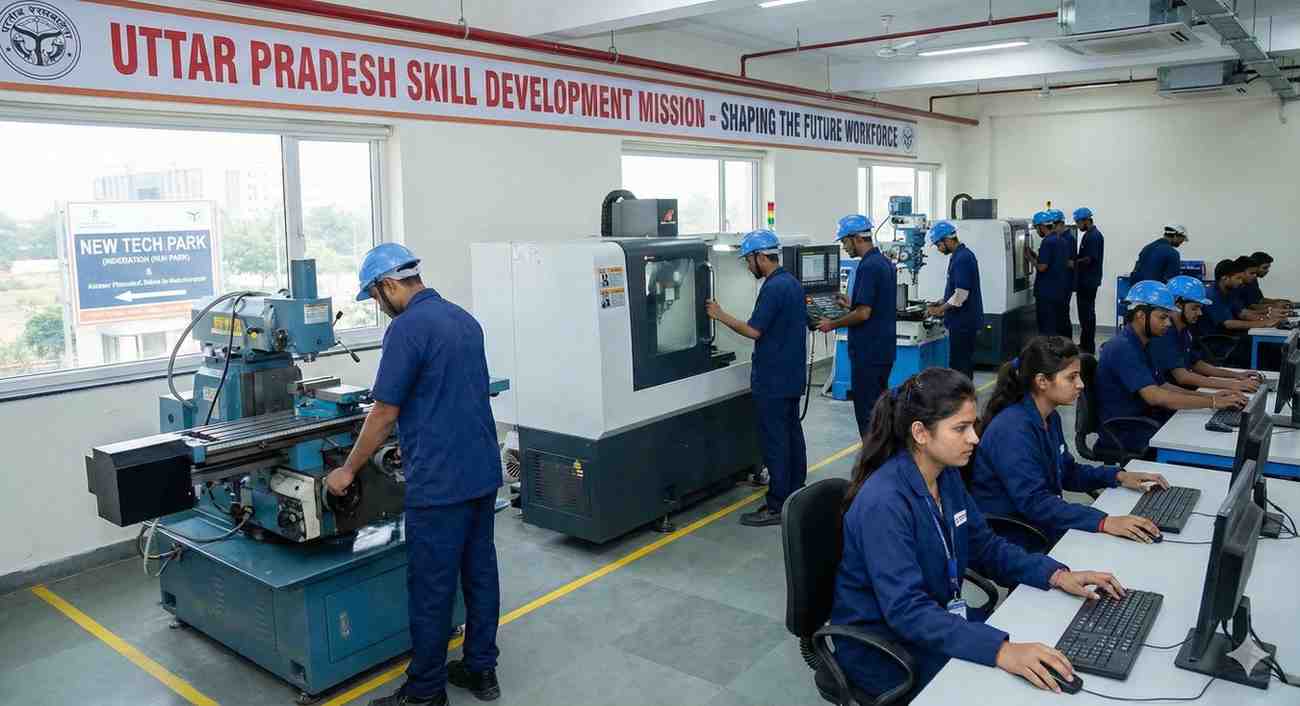
The Uttar Pradesh Skill Development Mission (UPSDM) has integrated vocational training into the school curriculum, targeting high-demand sectors such as healthcare, information technology, and manufacturing. By imparting market-relevant skills, this initiative aims to prepare students for both higher education and direct entry into the workforce.
4. Socio-Economic Support Programs
To mitigate socio-economic barriers, the government provides free uniforms, textbooks, and midday meals to students from economically weaker sections. As of 2023, official data shows a 20% increase in enrollment over the past five years, attributed to these supportive measures.
Impact on Workforce Development
1. Enhanced Enrollment and Retention
Efforts to improve basic education have resulted in higher enrollment rates, particularly among marginalized communities. Data from the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE) reveals that UP’s gross enrollment ratio (GER) for primary education reached 98.2% in 2023. However, retention remains a challenge at the secondary and higher education levels.
2. Narrowing Urban-Rural Disparities
Operation Kayakalp has contributed to reducing the quality gap between urban and rural schools. Despite these gains, issues such as teacher-student ratios and access to advanced resources persist, particularly in remote regions.
3. Improved Employability Through Skills
Vocational training initiatives have enhanced employability for high school graduates. According to the UPSDM, over 1 million students have completed vocational courses since 2019, with 65% successfully entering employment or pursuing advanced education in relevant fields.
4. Advancing Digital Literacy
The integration of smart classrooms has significantly boosted digital literacy, equipping students with critical skills for the modern workforce. However, rural areas continue to face challenges such as inadequate internet connectivity and insufficient teacher training for effective technology use.
Challenges and Recommendations
- Retention in Secondary and Higher Education: Address dropout rates by implementing targeted scholarships, mentorship programs, and career counseling to keep students engaged beyond primary education.
- Teacher Training and Resource Allocation: Enhance teacher recruitment and training, particularly in rural areas, to improve educational quality and ensure equitable resource distribution.
- Infrastructure Development: Expand access to basic and advanced infrastructure, including digital tools, reliable electricity, and transportation, especially in underserved regions.
- Continuous Monitoring and Impact Assessment: Establish comprehensive monitoring frameworks to evaluate the effectiveness of reforms and make data-driven adjustments.
Conclusion
Education reforms in Uttar Pradesh have made significant strides in addressing systemic challenges, particularly in increasing enrollment, modernizing infrastructure, and integrating vocational training. However, persistent issues such as dropout rates, quality disparities, and resource inequities must be addressed to fully realize the potential of these initiatives. By fostering inclusive, technology-driven education, UP has the opportunity to develop a skilled workforce capable of driving the state’s socio-economic growth and positioning itself as a leader in India’s evolving economy.